Introduction to Tesla’s New Factory
Tesla, a pioneer in the electric vehicle industry, has recently announced the opening of a new factory that marks a significant milestone in its growth and expansion strategy. This facility is located strategically to bolster Tesla’s production capabilities, with a specific focus on manufacturing batteries and electric vehicles to meet the rising global demand for sustainable transportation solutions. The company’s mission aligns seamlessly with current trends toward environmental responsibility, positioning Tesla to not only lead in vehicle production but also contribute to the overarching goal of sustainable energy.
This new factory plays a critical role in Tesla’s ambition to ramp up production volumes, rapidly scaling its manufacturing processes to support burgeoning demand for its innovative electric vehicles. It aims to produce thousands of units annually, thereby enhancing Tesla’s competitive edge in the automotive market. The facility is equipped with advanced technology, enabling efficiency and sustainability, which remain at the core of Tesla’s operations.
Moreover, the new factory underscores the company’s commitment to local economies by creating job opportunities and fostering an ecosystem of suppliers and partners. This not only strengthens Tesla’s operational footprint but also enhances its community engagement, which is vital for the company’s reputation and customer loyalty.
As Tesla embarks on this new chapter, the factory’s security becomes paramount, particularly regarding the perimeter fencing to safeguard assets and maintain operational integrity. This brings us to an essential component of the factory’s construction—security measures such as the Chinese-made 358 fencing, designed to protect the innovative products being developed within its walls.
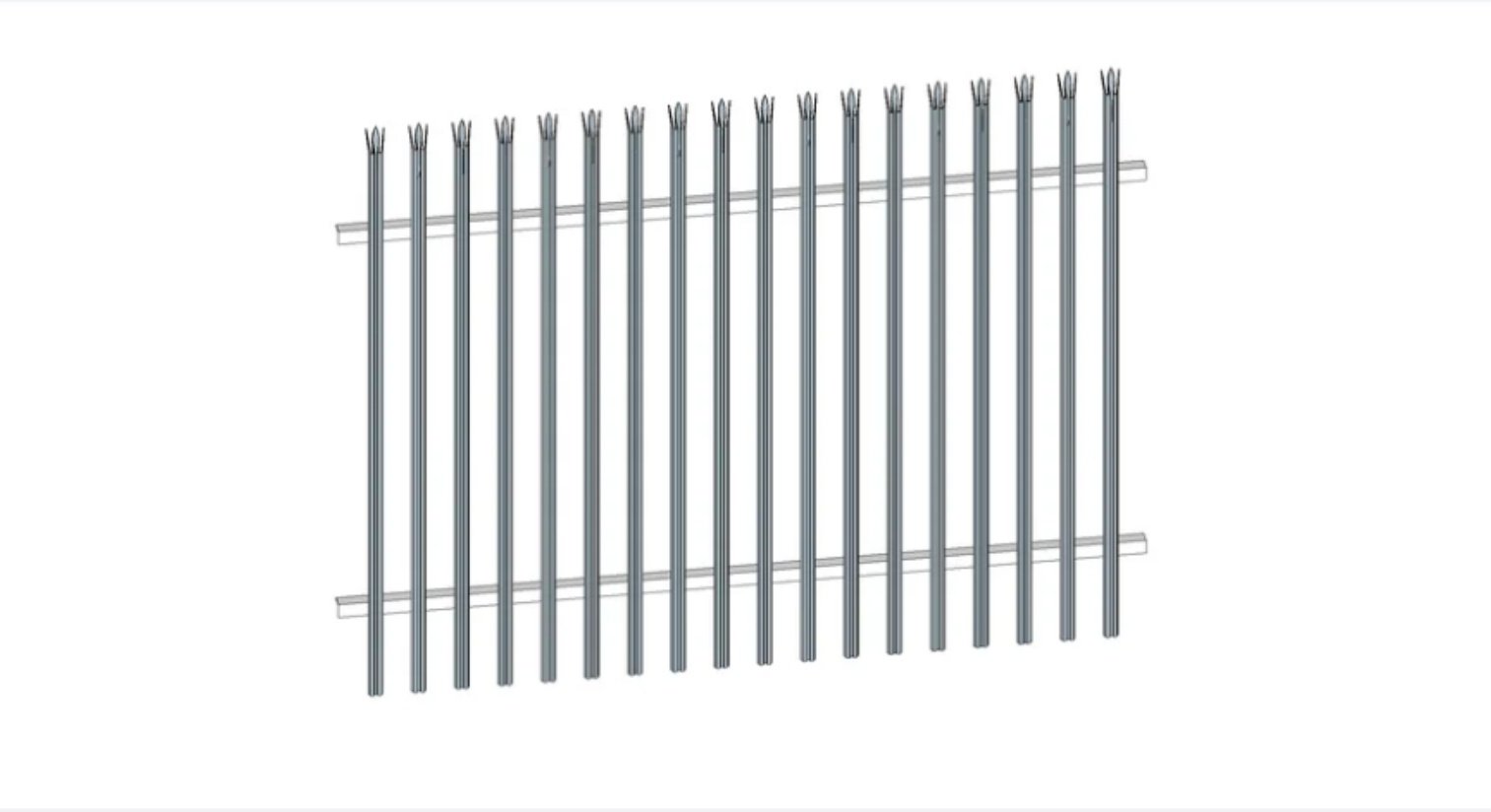
What is 358 Fencing and Why is it Used?
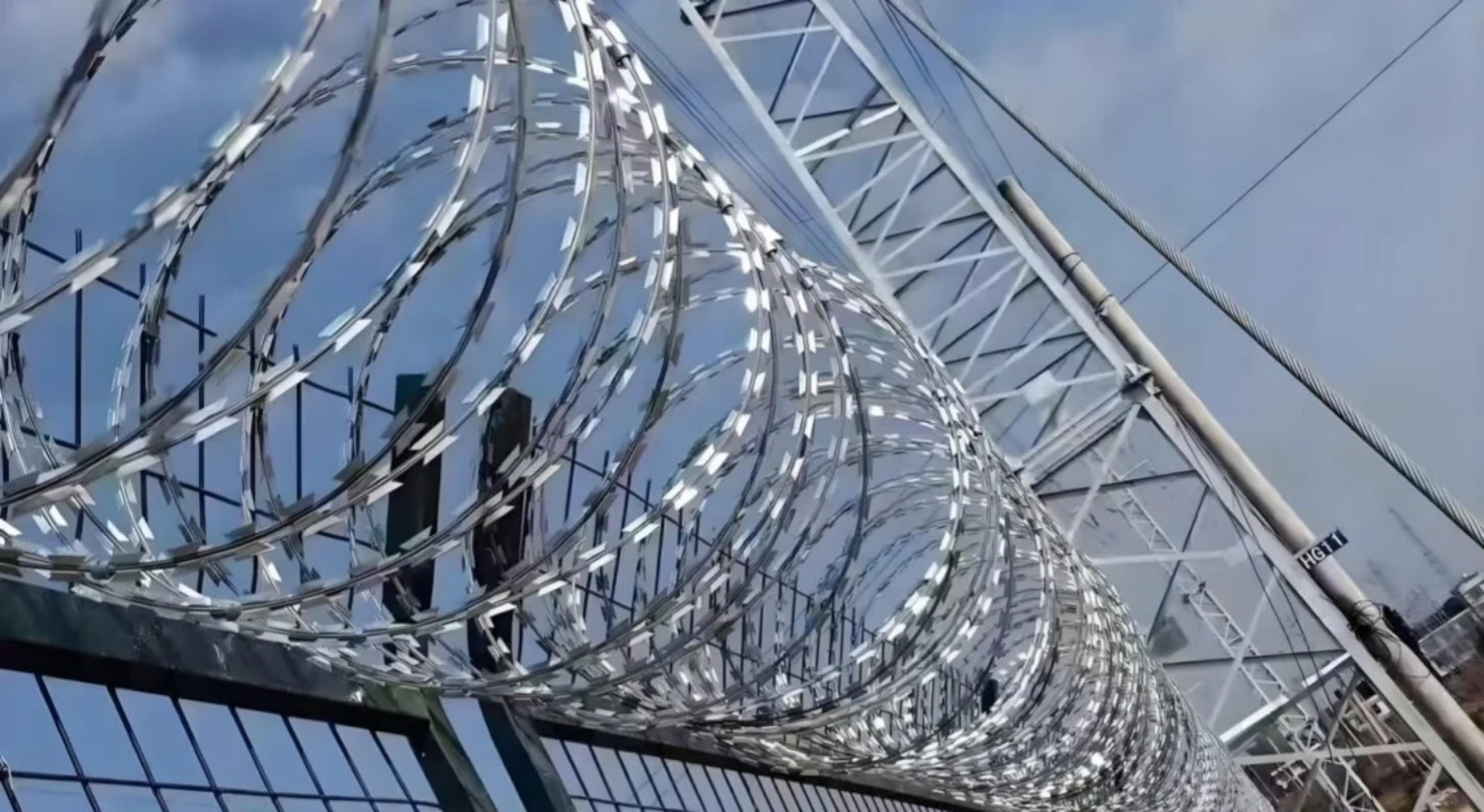
358 fencing, often referred to as prison mesh or high-security fencing, is a type of welded wire mesh fencing that has become increasingly popular in sectors requiring stringent security measures. Its name derives from its specifications: 3 inches by 0.5 inches, and 8-gauge wire. This fencing typically features a unique design that incorporates vertical and horizontal wires, forming a grid pattern that is difficult to climb or cut. The mesh itself is usually 358 millimeters in height and is made from high-quality steel, providing enhanced strength and durability.
One of the primary advantages of 358 fencing is its ability to deter unauthorized access, making it ideal for high-security environments such as manufacturing plants, prisons, and military installations. The tight mesh spacing minimizes footholds and handgrips, which effectively prevents intruders from scaling the fence. Additionally, its robust structure offers significant resistance against cutting tools, dissuading potential intruders from breaching the perimeter.
In terms of materials, 358 fencing is often galvanized or powder-coated, enhancing its durability and longevity against environmental elements. This resistance to corrosion and rust makes it particularly suitable for outdoor installations, where exposure to weather can lead to deterioration of lesser quality fencing options. The aesthetic appeal of powder-coated options can also blend seamlessly into various environments, thereby contributing to the overall visual integrity of the facility.
Moreover, 358 fencing is designed with security in mind, featuring the option for integration with advanced surveillance systems like cameras and alarms, further adding layers of protection for valuable assets. Its robust properties and design make it an optimal choice for facilities producing high-value goods, such as electric vehicles, ensuring that the premises remain secure against potential threats while maintaining operational safety.
The Role of the Chinese Fence Maker in Tesla’s Security Strategy
Tesla’s decision to source 358 fencing from a Chinese manufacturer underscores its strategic emphasis on security and cost-efficiency. The 358 fencing, renowned for its durability and security features, effectively serves as a critical line of defense at Tesla’s new factory. By partnering with a reliable manufacturer in China, Tesla leverages not only the competitive pricing associated with Chinese production but also the elevated standards of quality that this specific fencing type offers.
One of the primary factors influencing Tesla’s sourcing strategy was the overall cost-effectiveness of partnering with a Chinese fence maker. In a global market where margins are increasingly tight, the affordability of manufacturing in China allows Tesla to allocate resources efficiently. The favorable economics of overseas sourcing can lead to substantial savings when fulfilling large-scale manufacturing needs. As such, the integration of the Chinese-manufactured 358 fencing fits seamlessly into Tesla’s budgetary framework while adhering to its high standards.
Moreover, the manufacturing capabilities of the Chinese company played a pivotal role in this partnership. Chinese manufacturers are known for their advanced production technologies and capacity to efficiently scale operations. This adaptability is particularly beneficial for Tesla, which requires a steady supply of security components to support its expansive growth strategy. The alignment of high-quality production with logistical considerations further enhances the attractiveness of this partnership.
In summary, the collaboration with a Chinese fence maker symbolizes Tesla’s broader global supply chain strategy. By establishing relationships with international suppliers, Tesla not only taps into regional production advantages but also fortifies its security measures through reliable fencing solutions. This strategic choice illustrates how Tesla continues to innovate and optimize its operational framework while sustaining its commitment to safety and security at its factories. The interplay of cost, quality, and logistical efficiency remains fundamental to their decision-making process.
Implications and Future Considerations
The decision by Tesla to implement Chinese-made 358 fencing in their new factory has broad implications that extend beyond mere logistics. Firstly, from a security standpoint, the choice raises questions regarding the integrity of using components sourced from foreign suppliers. Stakeholders might question whether Chinese-made fencing offers the same level of security and reliability as domestically produced alternatives. The implications here are substantial, particularly for a company that prioritizes advanced technology and unwavering safety standards in its production facilities.
Moreover, this decision could influence international trade relations, particularly as tensions between the United States and China continue to evolve. While many businesses are navigating the complexities of global supply chains, Tesla’s choice to source fencing from China can be interpreted in various ways. On one hand, it may reflect a pragmatic approach to cost efficiency; on the other, it risks being viewed as a lapse in prioritizing local manufacturing, which could lead to criticisms from policymakers and consumers alike. In an era where ‘buying local’ has become a crucial mantra for many, Tesla may need to carefully manage its narrative.
The impact on Tesla’s public image cannot be understated. The company has built a brand synonymous with innovation and environmental stewardship. Therefore, the use of components from abroad, especially from a country often scrutinized for its labor practices and regulatory standards, may generate mixed reactions from consumers and investors. To mitigate potential backlash, Tesla will need to communicate transparently about their choice, emphasizing their commitment to quality and security while also acknowledging the realities of global commerce.
Looking ahead, future considerations must include a more robust strategy regarding manufacturing sourcing and security. As the electric vehicle industry continues to expand, companies like Tesla will have to balance cost with quality and ethical production practices. The dynamics of global supply chains are shifting, and companies must adapt to maintain their competitiveness while upholding their reputational standards.